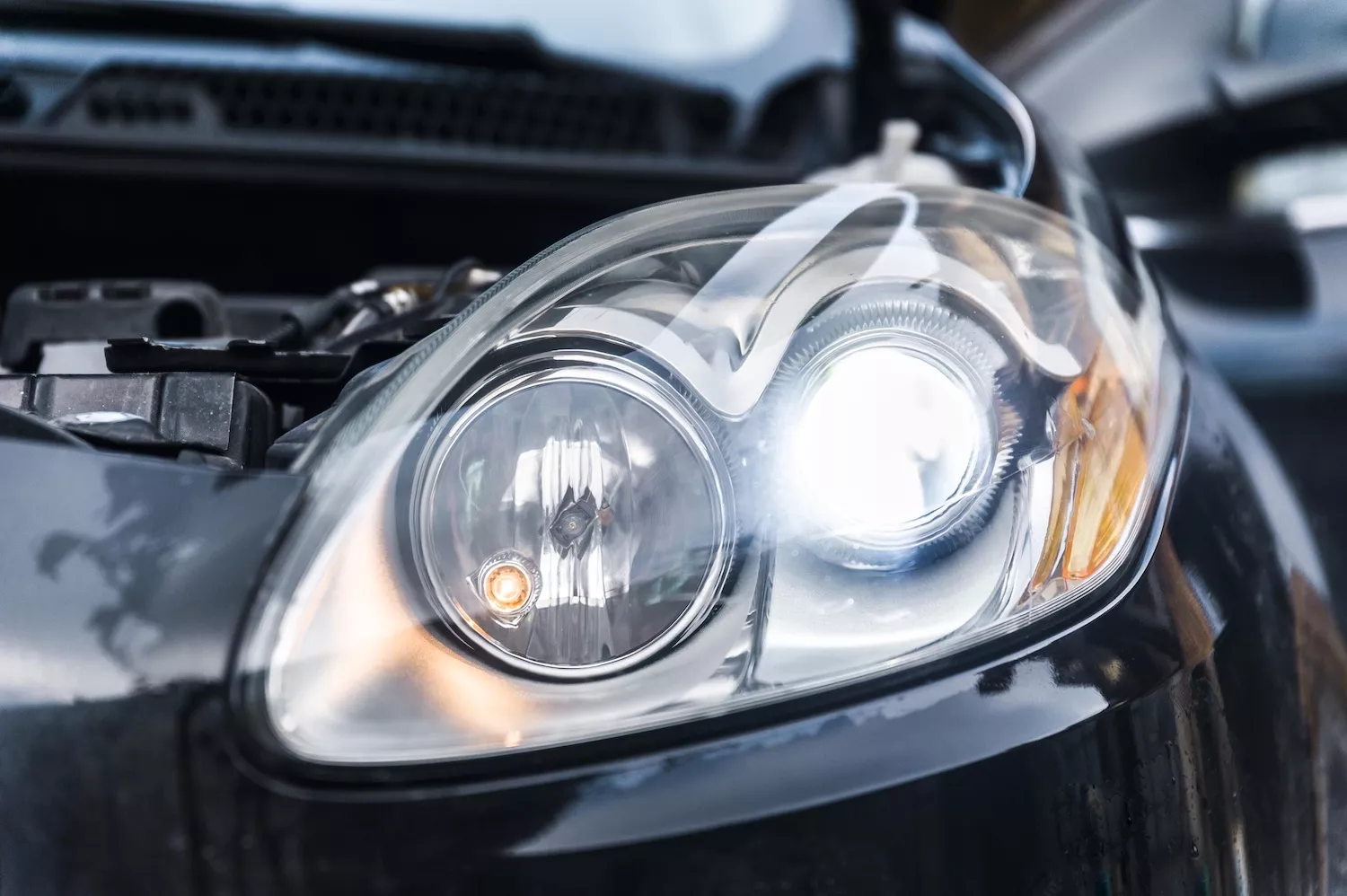
Driving at night or in heavy fog becomes dangerous when your car’s headlights are not working as they should.
For many drivers, the problem isn’t the bulb itself; it’s a damaged or failing part inside the headlight assembly.
Understanding the parts of a headlight helps you quickly identify problems, decide whether a repair or full replacement is needed, and choose the right aftermarket headlight assembly.
In this guide, we explain:
- What are the parts of a headlight
- How a headlight assembly works
- Which headlight parts fail most often
- and whether individual headlight components can be replaced
We’ll uncover the primary parts of a headlight and its role in producing the lights that have made nighttime driving safer. Buckle up, and let’s explore the inner workings of these illuminating marvels!
What Is a Headlight Assembly?
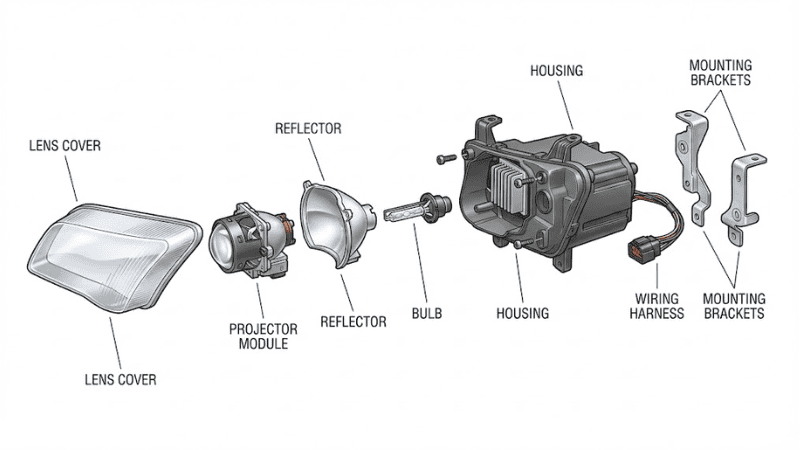
A headlight assembly, commonly referred to as a headlamp or simply a headlight, is an essential component of a vehicle. It’s mounted at the front to illuminate the road ahead.
These lights are critical for ensuring that the driver can see the path clearly, especially during nighttime or in low-visibility conditions such as fog, rain, or snow.
This distinction is important, as the headlight’s effectiveness is directly related to its design and functionality.
The importance of headlights extends beyond just providing light; they are a key safety feature of any vehicle. Here’s why they are crucial:
- Illumination: Headlights illuminate the road ahead, allowing drivers to see obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles in the dark.
- Visibility to Others: They ensure your vehicle is visible to other drivers, reducing the risk of collisions.
- Navigation: Headlights assist in navigating through curves, dips, and uneven terrains by highlighting the path.
- Signaling: Headlights, especially high beams and fog lights, are used to signal other drivers of your presence or to communicate during adverse conditions.
Without adequately functioning headlights, driving at night or in poor weather conditions would be incredibly dangerous.
They are designed to provide the right amount of light at the right angle to ensure both the driver and other road users remain safe. Ensuring that your headlights are well-maintained and properly aligned is crucial for safe driving.
The Core Components of a Headlight Assembly
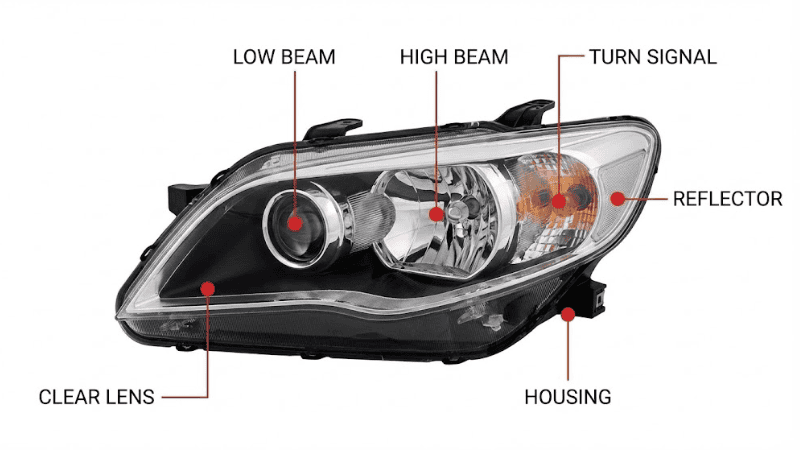
Headlamps are essential components of a vehicle’s lighting system, comprising several vital elements that work together to provide adequate illumination. Here’s a simple breakdown of each component and its function:
Lightbulb
The lightbulb is the light source in a headlamp. It produces a beam of light that illuminates the road. Different types of bulbs, such as halogen, LED, or HID headlights, affect the brightness and color of the light.
Electric Wires
These wires carry electrical current from the vehicle’s power source to the lightbulb, ensuring that the bulb receives the necessary power to produce light. In advanced vehicles, wires carry electric current to motors, sensors, moving panels, etc.
Reflective Glass
The reflective glass, often found inside the headlamp assembly, helps direct and focus the light from the bulb into a specific beam pattern. It concentrates scattered light rays from the headlight bulb and orients them in one direction.
Shielding Glass or Plastic Cover Lenses
This is the outer layer of the headlamp. It protects the internal components from dust, debris, and weather elements. The shielding surface also helps to ensure that the light beam is projected correctly and does not scatter unnecessarily.
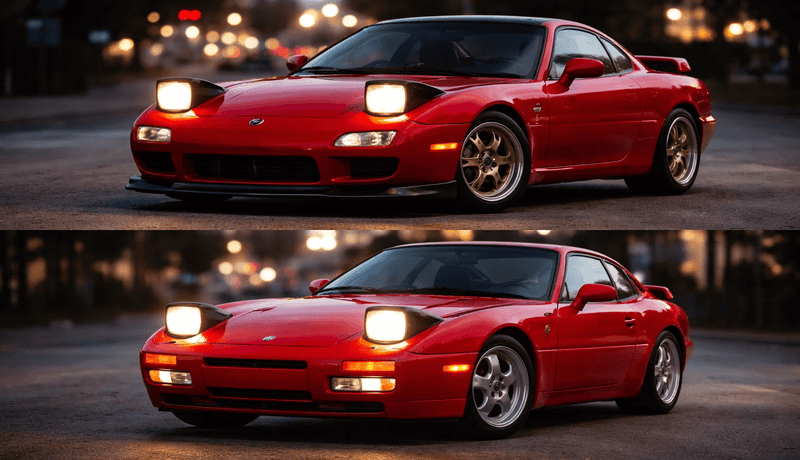
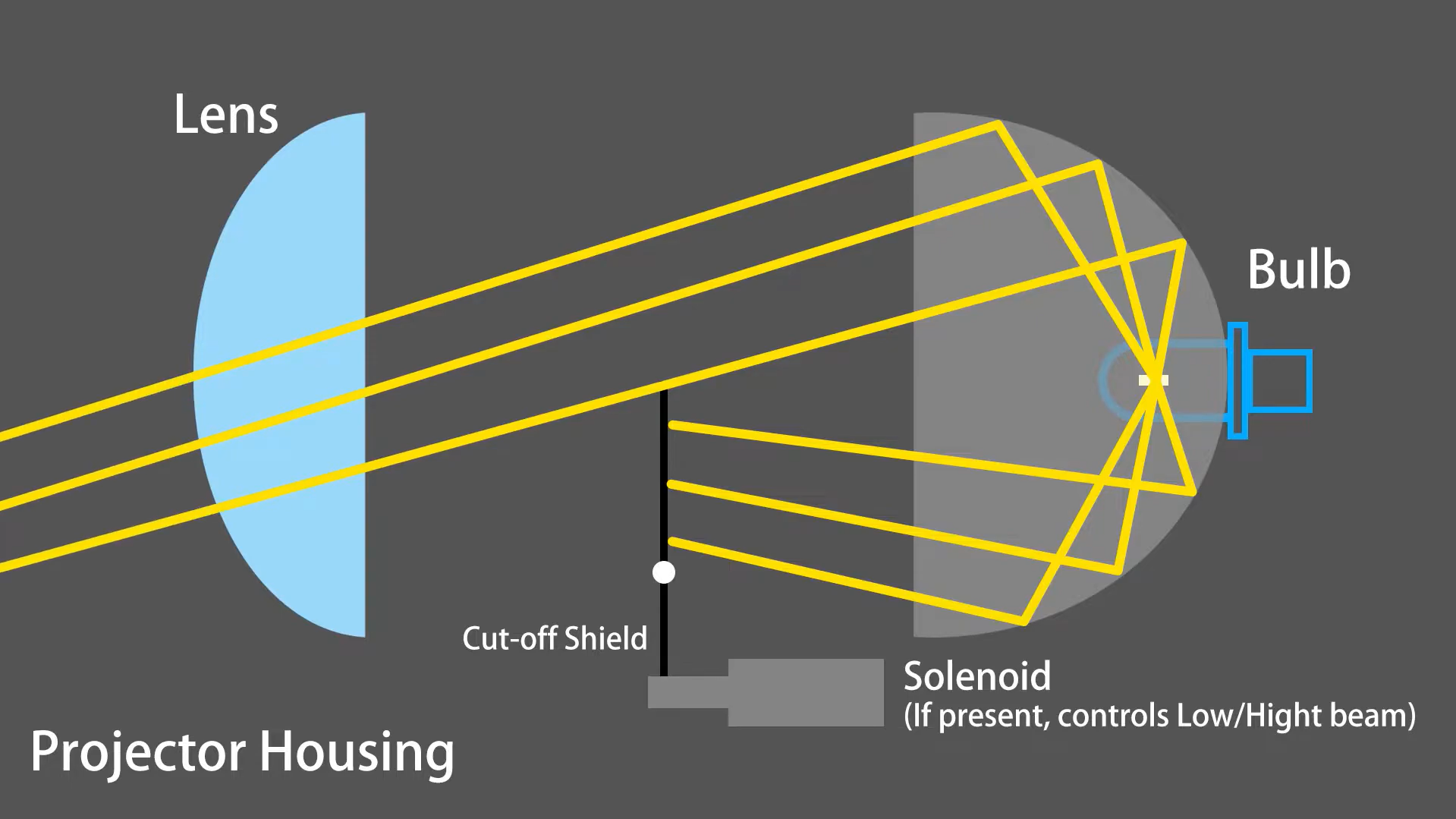
1. Headlight Housing
Headlight Housing Types: Reflector vs. Projector
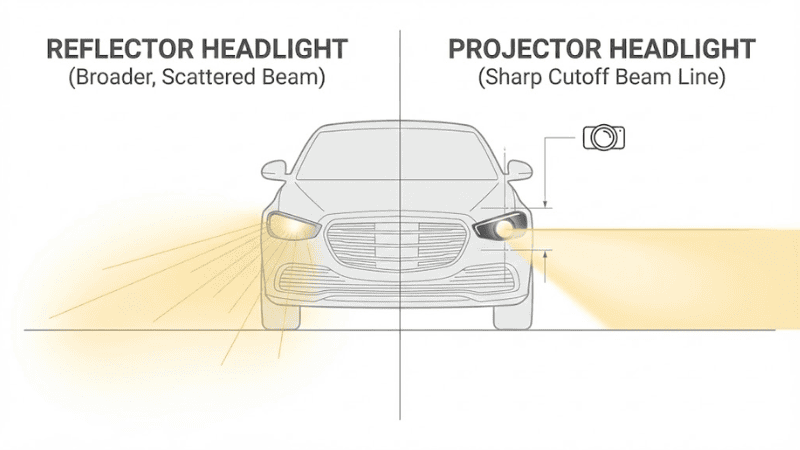
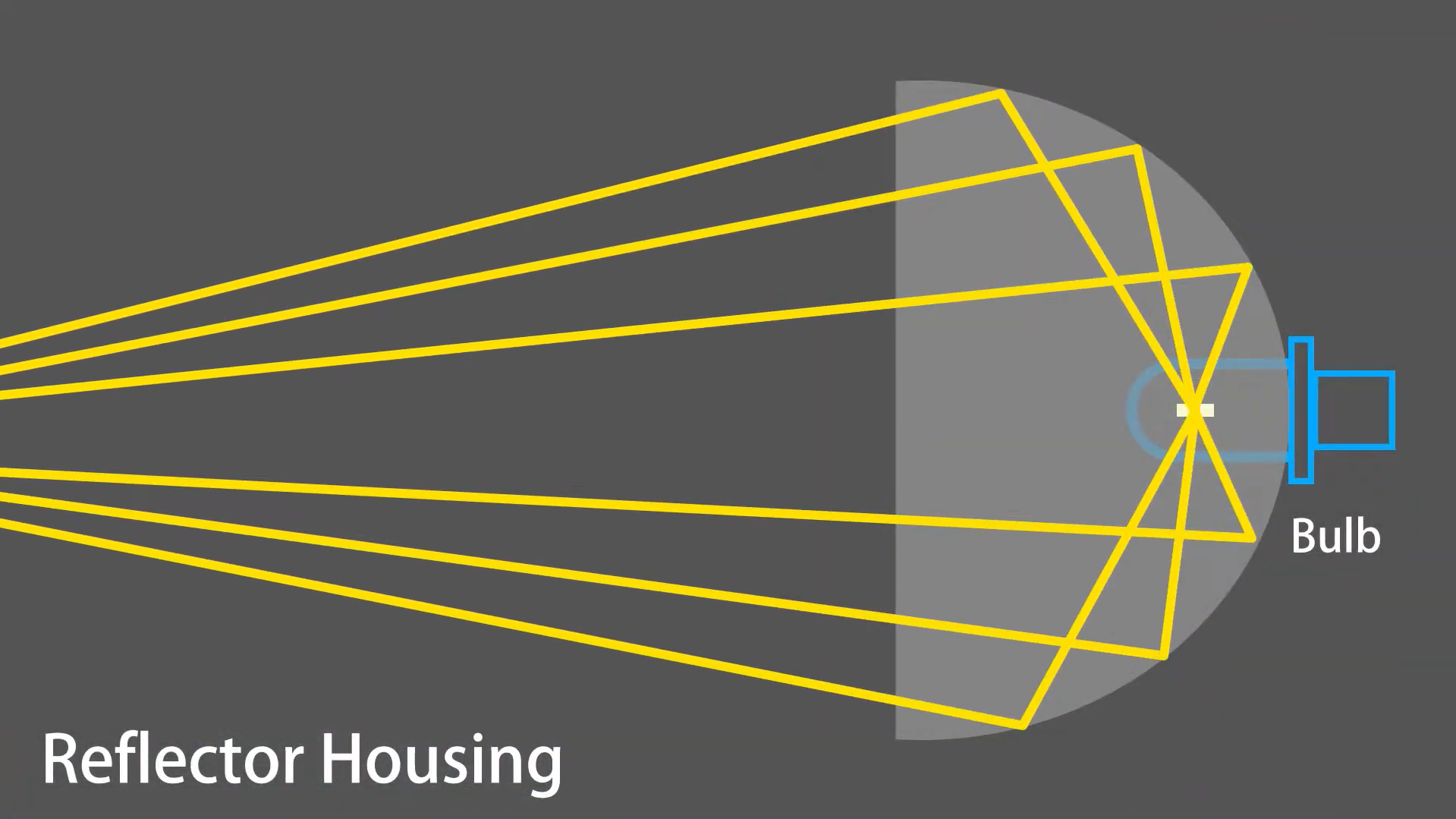
Reflector Housing:
Before 1985, the standard design for vehicle headlights was a reflector housing. This housing consists of a reflective surface positioned behind the bulb, known as the reflector. The reflector directs and distributes light.
The reflector ensures that the light emitted by the bulb is evenly spread across the road. A regular bulb emits rays in all directions, which means the bulb lights up everything around it, but the brightness remains unsatisfactory.
By bouncing light off its curved surface, the reflector creates a focused beam that is brighter and far more practical than the bulb itself. This design was adequate for its time, providing a reliable way to light up the road. However, it has since been largely replaced by more advanced headlight technologies.
- Advantages:
- Simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
- Wide coverage area.
- Limitations:
- Less precise light control compared to the projector housing.
- May cause glare for oncoming drivers.
- Common Applications: Older vehicles and budget-friendly models.
Projector Housing:
Projector housing, introduced in the 1980s, has become the standard in newer cars. This design employs a dedicated cover lens system known as the projector to create a sharp, well-defined beam of light.
The projector lens focuses the light emitted by the bulb, resulting in a more controlled and precise beam pattern compared to earlier reflector designs.
This enhanced control improves visibility and reduces glare for oncoming drivers. Light concentration by the inner lens is more efficient than that of a reflector. Projector headlights offer superior light distribution and illuminate more effectively, which enhances overall driving safety and performance.
- Advantages:
- Precise light output with minimal scatter.
- Reduced glare for other drivers.
- Enhanced aesthetics.
- Limitations:
- Slightly higher cost.
- Common Applications: Newer cars, luxury vehicles, and performance models.
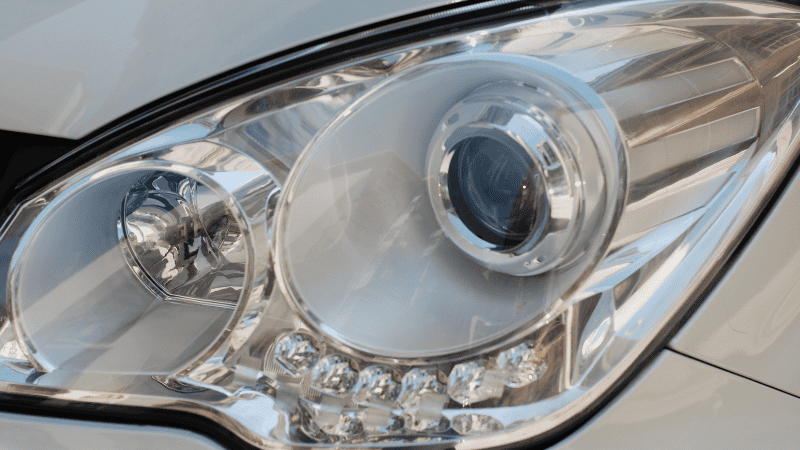
When Good Housings Go Bad
Common problems:
- Cracked housing after minor collisions
- Moisture or condensation inside the headlight
- Broken mounting tabs are causing misalignment
Common Damage Signs
Headlight housings take a beating. The most common issues are cracked lenses from rocks or broken mounting tabs that make the light wobble.
Moisture & Condensation
If you see water or fog inside the headlight lens, the seal has failed. This moisture will destroy the reflective coating inside. Unfortunately, you usually can’t fix just the seal; replacing the entire headlight assembly is the only permanent fix.
Material Selection for Headlight Housing

The headlight housing holds the bulbs securely within the vehicle’s body while shielding them from external elements. Materials for headlight housings vary based on their functional and aesthetic requirements.
Materials Used:
- Plastic (Polycarbonate): This material is commonly used due to its lightweight and impact-resistant properties. It’s cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, making it a popular choice for modern headlight designs.
- Glass: Although traditional and known for its clarity, glass is less common today because it is heavier and more fragile compared to plastic alternatives.
- Composite Materials: High-end vehicles often use composite materials such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers. They help make the headlight assemblies lightweight and durable.
Design Considerations:
- Aesthetics: While clear lenses are standard, some designs incorporate textured or patterned lenses to enhance visual appeal.
- Sealing: Effective sealing is essential to prevent moisture and dust from entering the housing, which can affect headlight performance.
- Alignment Adjustments: Many headlight housings include provisions for minor alignment adjustments at the back, allowing for precise headlight alignment to ensure optimal illumination.
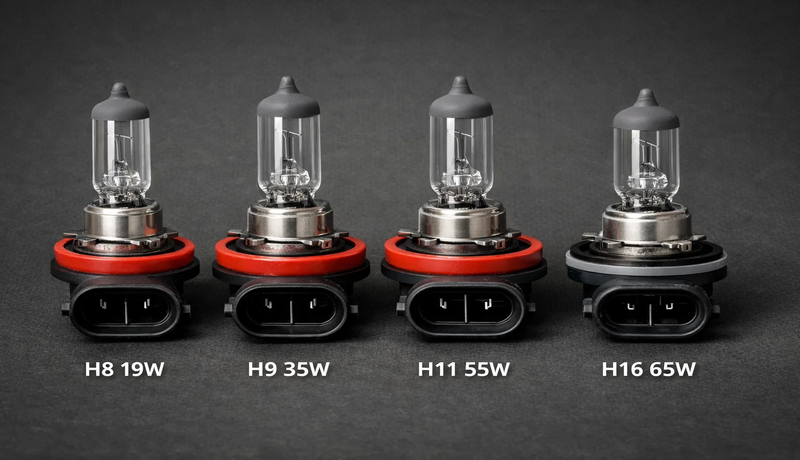
2. Headlight Bulbs
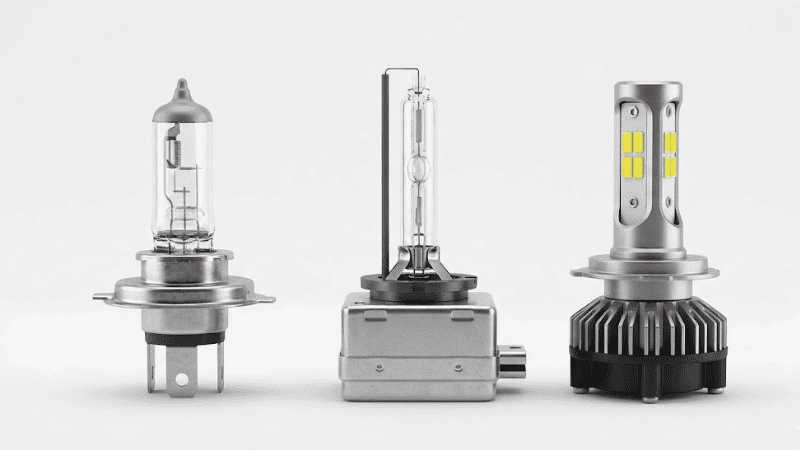
Headlamps are the core of a headlight system. The following headlamp systems are the most popular and widely used.
Halogen Headlights
Halogen Headlights use a tungsten filament enclosed in a glass capsule filled with halogen gas to increase efficiency and lifespan. An electric current passes through the material and heats it, eventually resulting in warm, yellowish light.
These bulbs typically last between 500 and 1,000 hours and have a Kelvin rating of around 3,200K to 3,500 K. The light output is about 700 to 1,200 lumens, depending on the specific bulb type.
HID Bulbs (High-Intensity Discharge)
HID Bulbs (High-Intensity Discharge) generate light by creating an electric arc between two electrodes within a chamber filled with xenon gas.
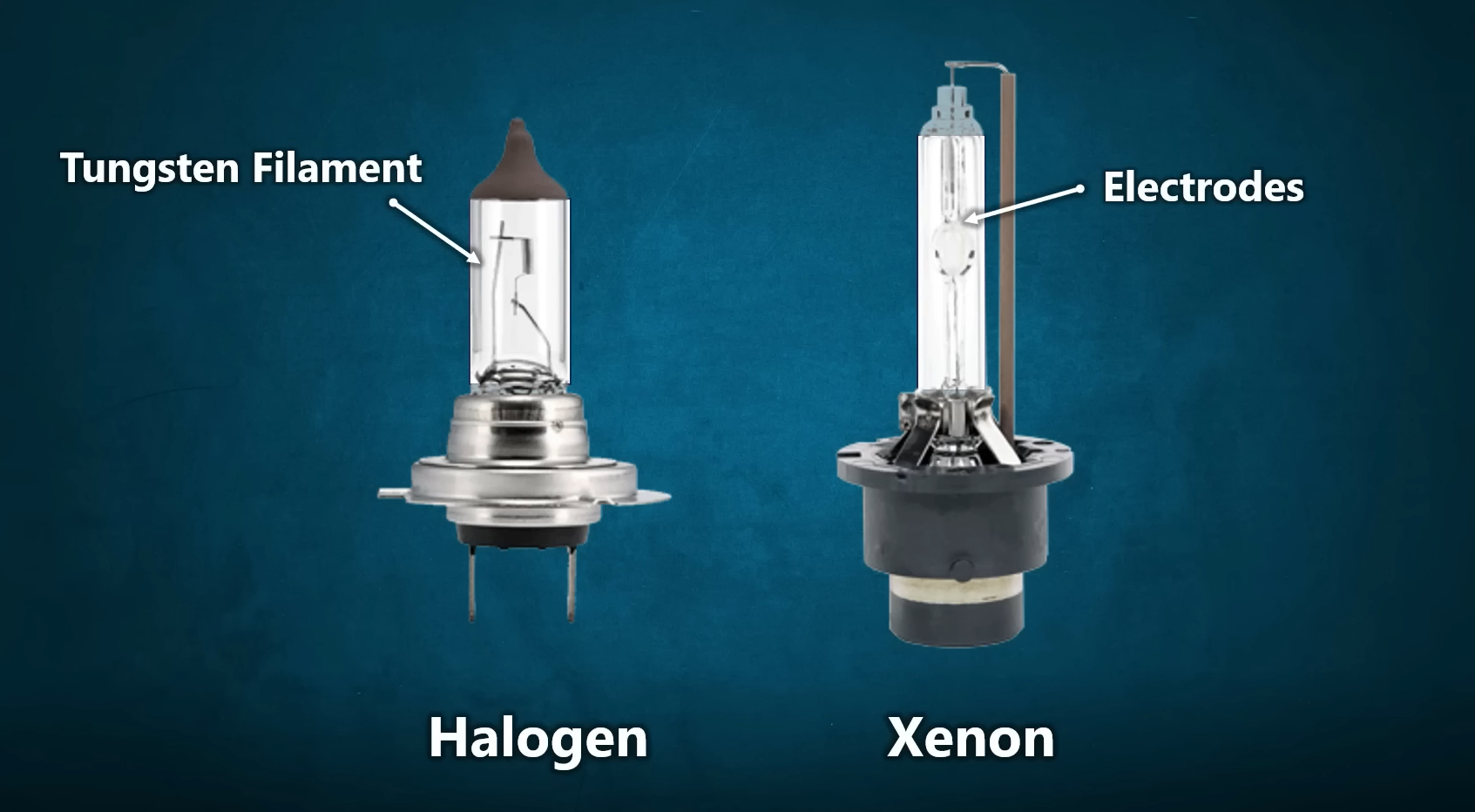
This method results in much brighter light compared to halogen bulbs, which have a lifespan of 2,000 to 3,000 hours. HID headlights offer a brighter, bluish-white light with a Kelvin range typically between 4,300K and 6,000K and produce between 3,000 and 5,000 lumens for superior illumination.
LED (Light Emitting Diode) Headlights
LED (Light Emitting Diode) Headlights use a semiconductor that emits light when an electric current passes through it. They are highly efficient, producing very little heat, and have the longest lifespan of up to 30,000 to 50,000 hours.
LED headlights generally produce a bright white light with a Kelvin range of 5,000K to 6,500K and offer around 2,000 to 4,000 lumens, providing excellent visibility with lower energy consumption.
If you’re an enthusiast, you might as well keep an eye out for Laser Headlights. They’re still relatively new technology but promise superior performance and efficiency to other bulbs.
| Feature | Halogen Headlights | HID (Xenon) Bulbs | LED Headlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brightness (Lumens) | 700 – 1,200 Lumens | 3,000 – 5,000 Lumens | 2,000 – 4,000 Lumens |
| Average Lifespan | 500 – 1,000 Hours | 2,000 – 3,000 Hours | 30,000 – 50,000 Hours |
| Kelvin (Color) | 3,200K – 3,500K | 4,300K – 6,000K | 5,000K – 6,500K |
| Efficiency | Low (Waste Heat) | Medium Efficiency | Highest Efficiency |
Importance of Proper Headlight Bulb Maintenance
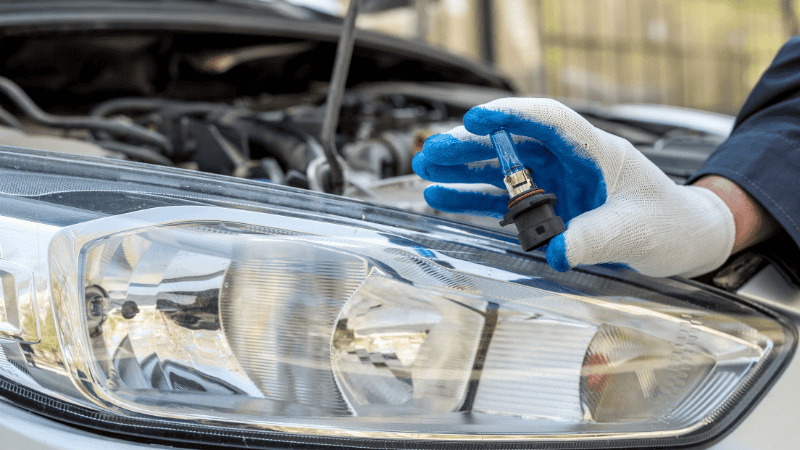

Regular inspection and maintenance of headlight bulbs are essential for ensuring safe driving conditions. By routinely checking your headlights, you can prevent flickering high beams, dead turn signal bulbs, and faulty brake lights.
Proper upkeep of your car’s headlights not only ensures that your vehicle remains visible to others but also keeps you safe from potential dangers.
How to tell if the bulb is the problem
If one headlight is dim or completely out while the lens is clear and dry, the bulb is usually the only part that needs replacement.
Can the bulb be replaced separately?
Yes. Headlight bulbs are the most commonly replaced headlight part and do not require replacing the full headlight assembly.
3. Headlight Lens
Material Selection for Cover Lenses
Headlight cover lenses come in two primary materials: glass and plastic, each with distinct characteristics and applications.
The glass was traditionally used as a headlight cover lens material. It has exceptional optical clarity and resistance to scratches. Glass lenses offer a streak-free, bubble-free surface, providing excellent transparency.
However, they have notable limitations, including being heavy and prone to shattering upon impact, which makes them less durable and more challenging to handle. These lenses were commonly found in older headlamp systems. Glass lenses show more dispersion optics than plastic lenses.
Nowadays, modern headlight cover lenses are mainly made of plastic, specifically polycarbonate (PC). Polycarbonate has become the material of choice for modern headlight assemblies. It is highly impact-resistant and ideal for automotive use. It is also much lighter than glass, reducing the overall weight of the vehicle.
Additionally, plastic lenses allow for smaller production tolerances that lead to more precise manufacturing. In modern vehicles, polycarbonate lenses are often used in various applications, such as inner lenses for low and high beams (bi-xenon) and fog lights.
These clear cover lenses, without optical elements, primarily protect the lights from soiling and harsh weather conditions.
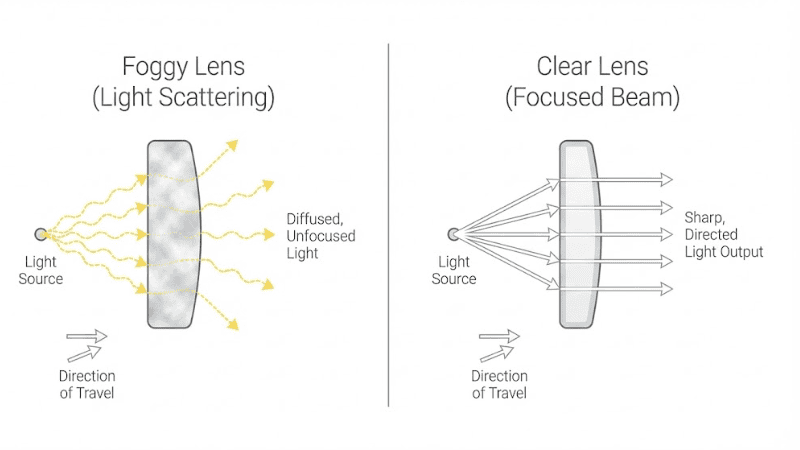
Importance of Headlight Lens Clarity
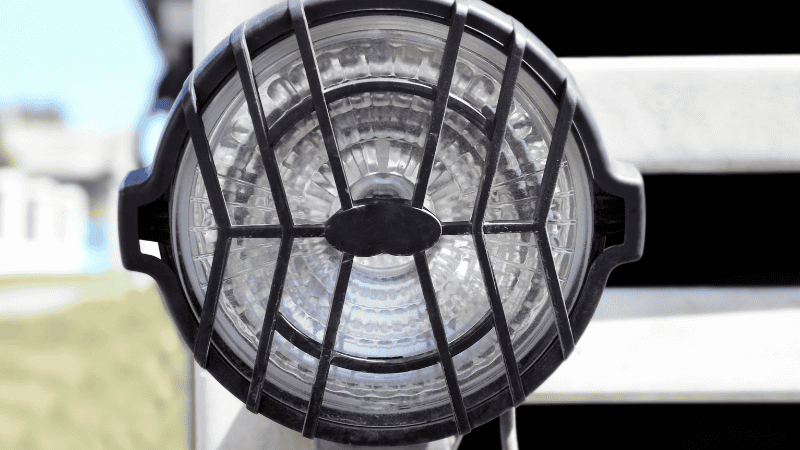

Clear headlight lenses ensure proper illumination and safe driving. Over time, lenses can become cloudy or hazy due to UV exposure and environmental factors such as dust, rain, fog, etc.
A hazy lens reduces light output and visibility. Sometimes, it may appear that your car headlight bulb is not working correctly or getting dimmer, but it may actually be because of the lens.
The foggy lens also impairs the driver’s ability to see the road and makes the vehicle less visible to others, increasing the risk of accidents. Consider wiping the lens with a dry cloth from time to time.
Common problems
- Foggy or yellowed lens from UV exposure
- Scratches reduce light output
- Water leaks caused by broken seals
How to tell it’s damaged
If the lens appears cloudy or yellow and light output is reduced even with a new bulb, the lens is the issue.
Can it be replaced separately?
On some vehicles, the lens can be restored or replaced. However, many modern cars require replacing the full headlight assembly.
4. Reflector VS Projection Modules
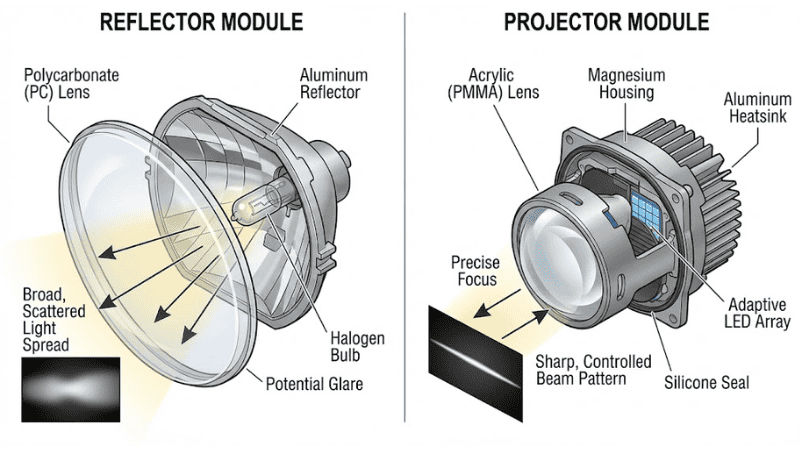
Material for Reflectors
Reflectors in headlights are typically made from thermoplastics due to their precise mold reproducibility. Materials like polycarbonate (PC) and acrylic (PMMA) are common.
PC is favored for its impact resistance, optical clarity, lightweight nature, and ability to withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for automotive lighting.
PMMA, on the other hand, is known for its high optical clarity and UV resistance, which are suitable for applications where light transmission and aesthetics are prioritized.
In high thermal stress situations, aluminum or magnesium may be used. Silicone is utilized in advanced LED systems for its flexibility and extreme temperature resistance.
Function and Importance of Projection Modules
Projection modules in today’s headlamps help car owners achieve precise beam patterns with high luminous flux collected.
These modules allow for more focused light distribution, reducing glare for oncoming traffic while illuminating the road ahead more effectively.
Their versatility supports a wide range of headlamp designs. Using them, manufacturers can implement advanced lighting technologies, such as adaptive headlights and LED systems, tailored to specific driving conditions and vehicle aesthetics.
What they do:
Both reflectors and projectors control how light is directed onto the road.
Key difference:
- Reflectors spread light broadly but may cause glare
- Projectors create a sharper, more controlled beam
When replacement is needed:
Damage to the reflector or projector usually requires replacing the entire headlight assembly.
5. Turn Signal and Other Components

Function and Importance of Turn Signal Bulb
Turn signal bulbs are necessary for signaling lane changes and turns as they help ensure communication with other car drivers.
A headlight assembly also includes the reflector, which directs light; the housing, which protects internal components; and mounting brackets, which secure the assembly to the vehicle. Each component plays a vital role in headlight functionality and vehicle safety.
Headlight Assembly Replacement
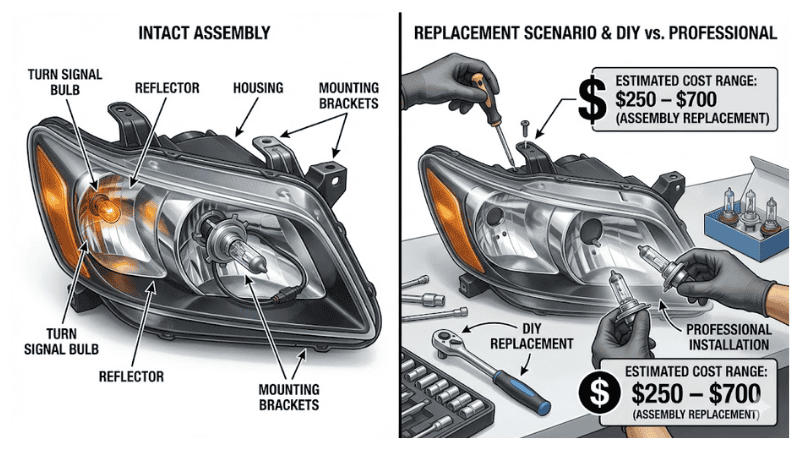
How Much Does a Headlight Assembly Replacement Cost?
The cost to replace a headlight assembly ranges from $250 to $700, with some shops charging up to $800 per assembly. The total cost depends on which components are damaged or faulty.
Labour costs are typically included if an auto repair performs the replacement. Depending on the build and price of the headlight bulb, the headlight reflector, and other components, the overall headlight assembly replacement cost can fluctuate.
Should You Choose DIY or Professional Headlight Replacement?
A DIYer with appropriate knowledge and tools can replace automotive lighting. However, changing a headlight bulb is more complex due to the involvement of additional components like the reflector, housing, and mounting brackets.
Professional replacement ensures proper installation and alignment, minimizing the risk of errors and potential safety issues.
How to Choose the Right Headlight Assembly
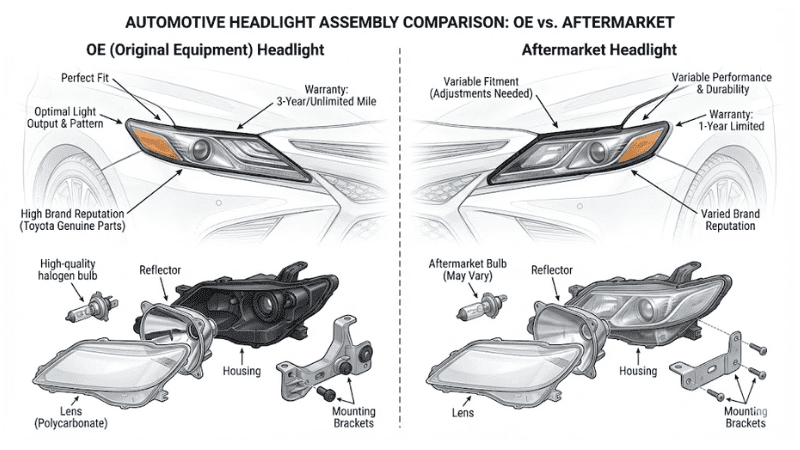
Vehicle Compatibility and OE vs. Aftermarket
When replacing a headlight assembly, check your vehicle’s year, make, and model to ensure compatibility. Both OE (Original Equipment) and premium aftermarket parts offer equivalent quality, fitment, and functionality.
When comparing OE (Original Equipment) and aftermarket parts, consider the following details:
- Quality: OE parts are typically manufactured to the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications, while aftermarket parts can vary in quality.
- Fitment: OE parts are designed for perfect fitment. Aftermarket parts may require adjustments.
- Warranty: OE parts usually come with a warranty from the vehicle manufacturer, whereas aftermarket parts may have varying warranty terms.
- Price: OE parts are often more expensive, while aftermarket parts can be more cost-effective but vary widely in price.
- Performance: OE parts match the vehicle’s original performance standards, while aftermarket parts may offer different performance characteristics.
- Brand Reputation: OE parts are from the vehicle’s original manufacturer, while aftermarket parts come from various manufacturers with differing reputations.
Conclusion
A headlight assembly is the most substantial part of a vehicle’s lighting system. Replacing it can improve visibility on dark roads and protect other connected components.
A DIY replacement effort can save you some money on labor costs. But if you’re driving an advanced vehicle, plug-and-play is not always streamlined.
Your Trusted Supplier for OEM-Compatible Headlight Assemblies
Whether you’re dealing with cracked housings, moisture damage, or outdated lighting systems, choosing the right headlight assembly makes all the difference in safety, performance, and long-term reliability.
Carlightvision supplies OEM-spec and premium aftermarket headlight assemblies with verified fitment, stable beam patterns, and consistent quality control—trusted by distributors, workshops, and automotive brands worldwide.
Contact us today to get technical support, compatibility confirmation, or a competitive quote tailored to your vehicle model or project needs.
FAQs About Headlight Parts
Q1: What are the main parts of a headlight?
A car headlight usually includes the bulb, lens, housing, reflector or projector, wiring, and mounting brackets. Each part affects how bright the light is and where it shines on the road.
Q2: How do I know if my headlight problem is the bulb or the assembly?
If only one headlight is out and the lens is clear and dry, it’s usually just the bulb. If both lights are dim, misaligned, or have moisture inside, the issue is likely with the headlight assembly.
Q3: Can I replace just the headlight lens?
Sometimes. On older vehicles, the lens can be replaced or restored. On many modern cars, the lens is sealed to the housing, so replacing the full headlight assembly is often required.
Q4: Is moisture inside the headlight a big problem?
Yes. Water inside the headlight damages the reflector and electrical parts. Once the seal fails, replacing the entire headlight assembly is usually the only long-term fix.
Q5: Are aftermarket headlight assemblies as good as OEM?
High-quality aftermarket headlight assemblies can match OEM fit and performance when they’re made for your exact vehicle model. Always check compatibility before buying.




