Choosing the best LED headlight bulbs is a detailed process. There are many issues to consider, including the bulb design, the quality of components, compatibility with your car, and local regulations.
This article aims to help you have an easier time when switching to LED headlights. We discuss the basics of these bulbs, the different types available today, and the crucial factors to consider before purchasing. Find out below how you can be a more savvy LED customer.
The Basics of LED Headlight Bulbs
The light from LED headlights comes from light-emitting diodes(LEDs). These are special semiconductors that emit light when an electric current passes through them.
Compared to other types of headlight bulbs, less of the energy that goes into LED headlight bulbs is dissipated as heat. This makes the bulbs more efficient and contributes to their longer lifespans.

The brightness of modern LED headlights is comparable to HIDs, and the light output of some is even greater. This is mostly a good thing, but it also contributes to the glare problem when the bulb is incorrectly installed or paired with the wrong headlight assembly.
LED headlight bulbs are not compatible with every vehicle’s headlight assembly. Some will require an LED headlight kit to function,n and for others, even this won’t be enough.
Types of LED Headlight Bulbs
There are different ways of classifying LED headlight bulbs. This is one reason why choosing the right LED headlight bulb is a challenge for many car owners. We discuss some of these classifications below.
Cooling System
LED bulbs can come with or without a fan. A fanless LED headlight bulb is cooled by thermal dissipation via a heat sink. The most common type of heat sink for fanless bulbs is rigid and made from an aluminum alloy, but other bulbs have the less common flexible tin-plated copper heat sink.
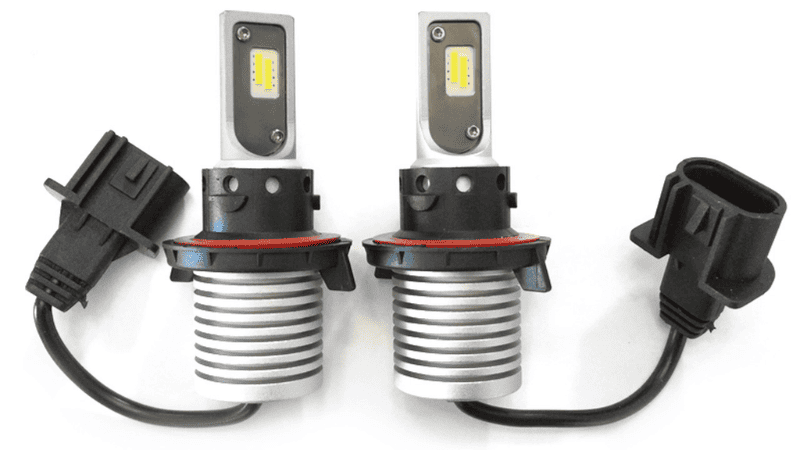

LED bulbs with fans offer the best cooling performance but the fans can be loud, depending on the manufacturing quality. If the fan fails, it can also compromise the whole bulb.
LED Chip Configuration and Position
When choosing an LED headlight bulb, drivers should also consider the LED chip’s position along the height of the bulb. 1:1 bulbs have chips that are roughly the same size as the filament in your original halogen bulbs and at a similar height. This increases compatibility with existing headlight housings.
The configuration of LED chips is also important. Some bulbs have chips on two sides only. This means they have to be precisely positioned with the LEDs at 9 and 3 O’clock for the best light output. Others have a 360 LED configuration and emit light equally in all directions.
LED Driver Location

The LED driver ensures the LED gets the correct type and amount of electricity it needs to function. They also protect them from voltage fluctuations. In some bulbs, these drivers are separate from the bulb, while in others, they are part of the bulb, i.e., inbuilt.
External drivers make bulbs bulkier, but this protects the driver from the heat emitted by the bulb. Inbuilt drivers make the bulbs compact, but the effect of heat on the driver can shorten the bulb’s lifespan, and these bulbs may not be as bright.
Single or Dual Beam
Some vehicles have separate bulbs for the high and low beams while others have the same bulb serving both purposes. This remains the case when you switch to LED headlights.
Therefore, if your car has dual-beam headlight bulbs, you’ll need a dual-beam LED light bulb. If your car has single-beam bulbs, you’ll need separate LED headlight bulbs for the low and high beams.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing LED Bulbs
If you want the best lighting experience when you buy LED bulbs, there are several factors you should consider. These factors range from the functional to the legal aspects of these bulbs.
1. Use High-Quality Chip
There are different types of LED chips used for automotive lighting. These chips have different levels of light output, cost, manufacturing complexity, etc. Some LED chip types you are likely to come across are:
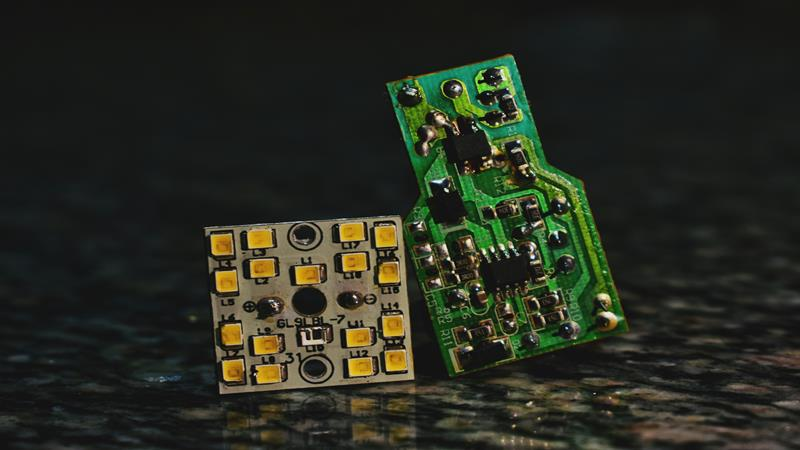

- CREE: CREE LED chips are known for their high brightness levels. They also emit light over a wider angle. These chips can, however, be expensive, and their light beam pattern isn’t great.
- Luxeon Z ES: These chips have an outstanding lifespan and heat resistance. They have a better light-beam pattern than CREE chips with a good cutoff. The downside of these chips is their higher cost.
- CSP: CSP chips are compact and cheap. Their small size has made them popular in LED headlights because they can be used to replicate the size and position of the filament in traditional headlights, resulting in a similar beam pattern. Unfortunately, their heat dissipation isn’t great.
- COB: These chips are bright and cheap but have poor light beam patterns, limited power, are harder to manufacture, and don’t dissipate heat well.
- Flip-Chip: Flip chips are hard to manufacture but their quality is consistent. They also have good beam patterns and are competitively priced.
As important as the quality of the chip is, even the best LED chips can’t guarantee you’ll get good-quality LED headlight bulbs. It’s important to consider how the headlight manufacturer uses the chip in the bulb.
2. Safe Light Beam Pattern
The light beam pattern will affect two important things:
- How well the headlights illuminate the road ahead
- How much glare the headlights cause for oncoming traffic
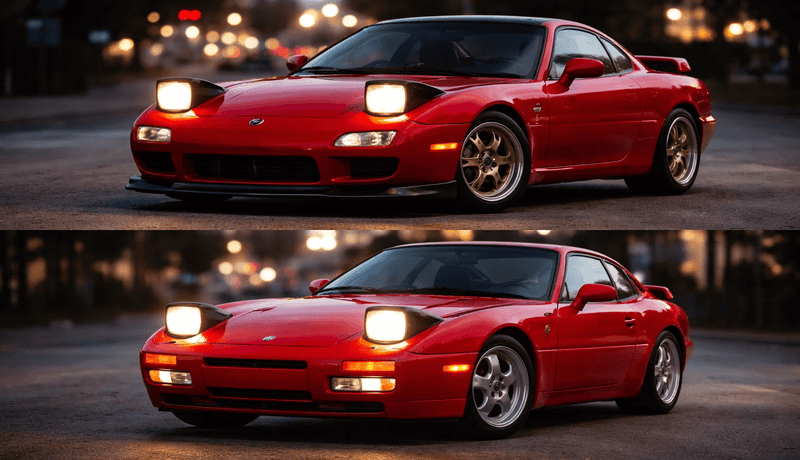
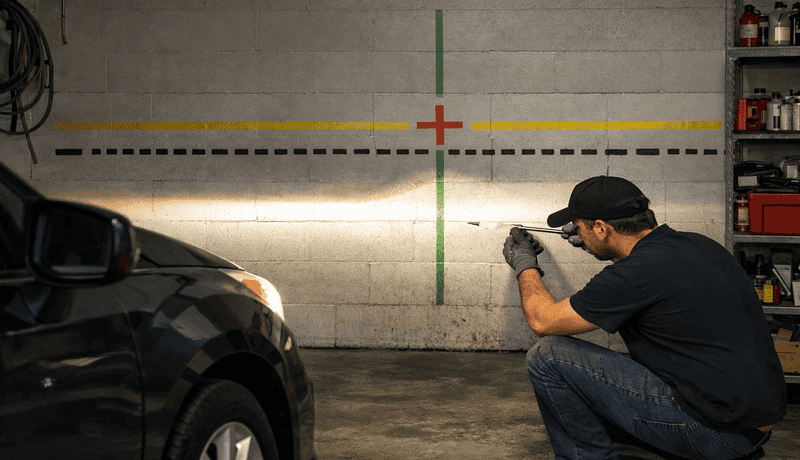
The light beam pattern can be determined by the housing of your headlight, the lens, the LED bulb design, or all three factors. This is why even the brightest LED headlight bulb can still give you a bad beam pattern if paired with an incompatible housing.
A good beam pattern has clear cut-off lines, good width, and good light distribution. This makes it easier to aim the headlights and limit the amount of glare on oncoming traffic. Some LED headlight bulbs have such poor beam patterns that no amount of aiming or adjusting will help.

The two main standards for beam patterns used in the world are the SAE or DOT standard and the ECE standard. The DOT standard is used in the US, while the ECE standard applies to most other countries in the world. Australia’s ADR standard is similar to the ECE.
3. 1:1 Design As Halogen
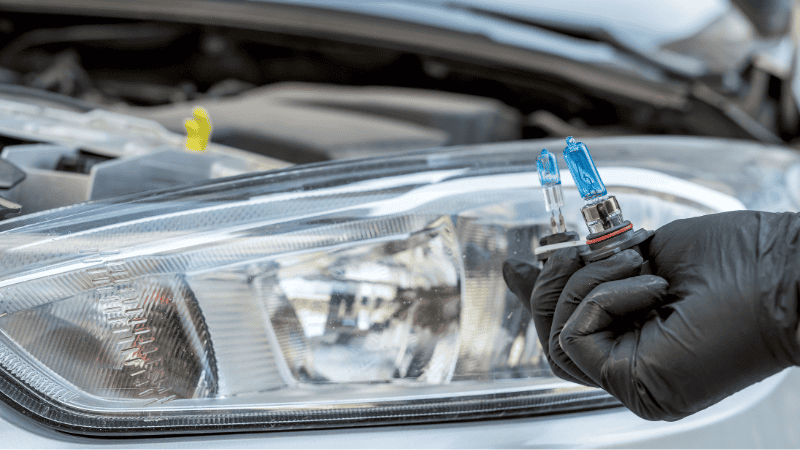

One cause of poor beam patterns when switching from halogen headlight bulbs to LEDs is the size and position of the LED.
In halogen bulbs, the filament serves as a point source that emits light in all directions. Additionally, the filament has a specific size and position inside the headlight housing. The headlight assembly is designed with this in mind.
If your chosen LED headlight bulb has a chip or chips that are wider or longer than the filament in your stock halogen bulbs, the light will not be cast in the same pattern. This problem will also be seen if the chip is higher up or lower along the length of the bulb.
When choosing an LED bulb, compare it with your existing halogen headlight bulb and check if the size and position of the chip are approximately the same. This is called a 1:1 design.
4. Right Color Temperature
LED bulbs can achieve a wider range of color temperatures compared to traditional halogens. However, you will find that most LED headlights in the market have a color temperature of between 4300K and 6500K. Three common options are explained below.

- 6500K is a good choice because this color temperature is close to natural daylight. This translates to great visibility when driving at night, and if you live in a sunny area, your eyes may be well-adjusted to this kind of light. The slightly cooler hue also gives your car a sleeker look.
- At 5800K, the light looks white and neutral. You get a good balance between visibility and aesthetics. Many OEMs opt for this color temperature because it causes less eye strain than 6500K.
- 4300K are considered warmer, and the light has a yellow hue. These have better penetrating power than 6500K lights, making them a better option when driving through fog, mist, or rain. These also produce less glare.
Although you will find 8000K and 10000K LED headlamps in the market, it’s probably not a good idea to get these. These bulbs produce blue lights and can cause more eye strain. The color blue is also associated with emergency vehicles, and this can confuse other drivers.
5. Effective Heat Dissipation
A commonly cited advantage of LEDs is that they produce very little heat. However, this is only in comparison to other types of headlight bulbs. In reality, between 60 and 95 percent of the power that goes into an LED is lost as heat.
This means that cooling is still a major consideration when choosing a good LED headlight bulb. As discussed above, all LED bulbs come with some kind of heat sink, and others have both a heat sink and a fan for better cooling.
Better heat dissipation will result in greater light output from your bulb. It will also result in better efficiency and increase the lifespan of your bulb. However, cooling systems such as fans can create another point of failure for the bulb and some fans are loud.
Large heat sinks may also make it harder to install the bulb. This means that when choosing an LED bulb, you’ll have to balance the effectiveness of the cooling solution with other practical considerations.
6. The Legality of LED Bulbs
There is no doubt that LED bulbs can significantly improve your driving experience. However, there is a chance that they may not yet be legal in your jurisdiction, depending on who installed them.
In some areas, LED headlights that the manufacturer installed are considered legal,l while aftermarket LED headlights are considered illegal. This is because manufacturer-installed LED headlights are working as they were engineered to, while aftermarket bulbs are a modification.
The issue of legality is also why using LED headlights with a blue hue on the road is not a great idea. This color is associated with emergency services and is likely to get you pulled over. Before buying an LED bulb to replace your halogen bulb, check your local laws and confirm whether this is permitted.

Additionally, you should also consider that one reason why aftermarket bulbs are not legal in many places is due to their effect on other motorists. Ensure your headlights are professionally installed and adjusted to limit this problem.
7. From a Well-Known Brand
Getting your headlights from a well-known brand helps to take much of the guesswork out of the process of choosing. An unknown manufacturer may make a lot of paper promises, but this does not mean they’ll be able to deliver on those promises.
A common issue with LED car light bulbs is the number of unknown brands that show up, sell some products, and disappear, often leaving many disappointed customers in their wake. This is less likely when buying LED bulbs from a well-known brand that has been built over several years.
A well-known brand such as Carlightvision understands that a series of disappointed customers will result in a bad reputation, and this will hurt the company’s business in the long run.
Conclusion
An LED headlight bulb can be a big upgrade if you’ve been using a halogen bulb. Unfortunately, choosing the right bulb is not easy in a market full of low-quality and incompatible options.
When choosing an LED headlight bulb, it helps to know how these bulbs operate and the impact of different features on the bulb’s performance. There are legal considerations to keep in mind as well. Ultimately, it always helps to start with a well-known brand in the LED headlight market.
Why is Carlightvision a Great Choice for LED Headlights?
Carlightvision is a well-known brand in the world of LED headlights. We have collaborated with reputable names such as Super Bright LEDs and Kerbl and have more than 15 years of experience manufacturing LED bulbs for ODM/OEM customers. Visit our website to find out which of our auto LED light bulb solutions is right for you. Contact us to get a price quote!