The LED chip is the heart of an LED light bulb. This includes LED bulbs used for automotive headlights. However, not every LED chip is built the same, nor do they perform at the same level. This is an important factor for suppliers of LED headlight bulbs to consider.
In this article, we will examine the characteristics of five commonly used LED chips for headlight bulbs. We’ll explain the unique features of each and their pros and cons. We’ll also explain LED chips and why you can’t always judge them based on size.
What are LED Chips?
LED is an acronym that stands for light-emitting diode. This unique name differentiates them from regular diodes that don’t produce visible light.
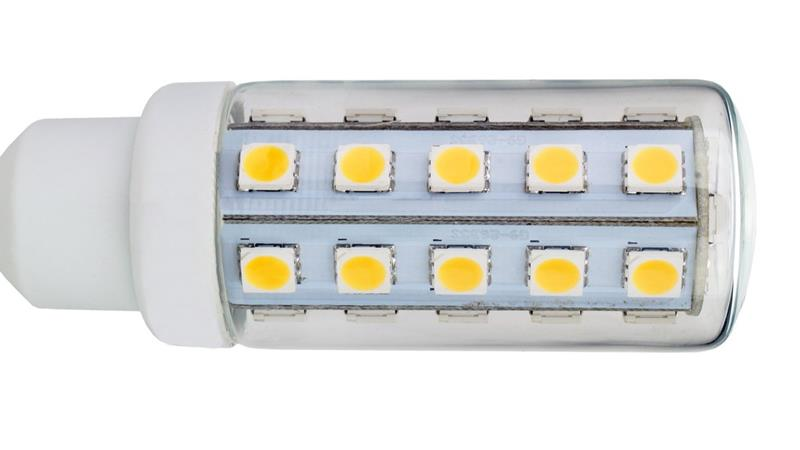

The Basics of LEDs
LED chips are diodes made using special semiconductor materials that emit light when a voltage is applied across them.
There are many types of diodes in existence today and they are used in many applications including communications, computing, and current conversion. However, LEDs differ from other diodes because they emit light.
All diodes release energy when electrons at a higher energy band combine with a hole and move into a lower energy band. Much of this energy is released as heat even in LEDs. However, a significant amount of this energy is also emitted as visible light in LEDs.
This unique behavior has led to the use of LED chips for illumination. They can be found in indoor lighting, street lights, LED strips, and automotive interior lights. More recently, automotive LED lighting has made its way to headlight bulbs.
Why Should You Use LEDs?
People are not just choosing LEDs because they are the newest, shiniest piece of tech. LED technology has significant advantages over conventional lighting technologies.
The most important advantage of LEDs is their energy efficiency. LEDs are more than 75% more efficient than incandescent bulbs. This translates to brighter bulbs and better fuel economy when LED bulbs are used in car headlights.
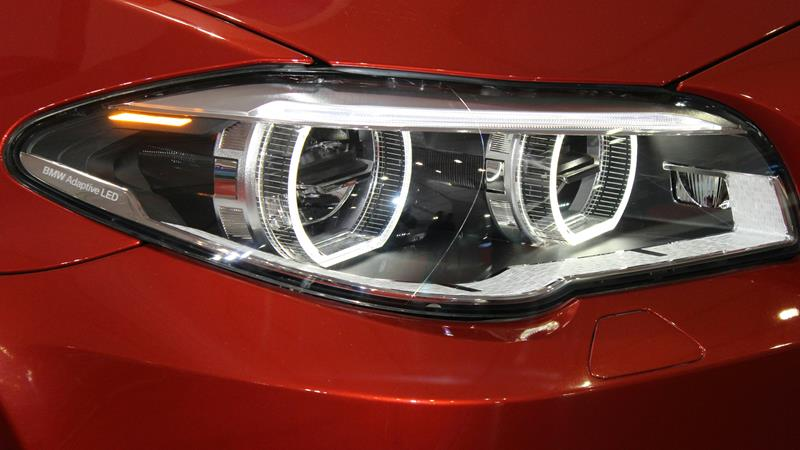

LED lights also emit less heat. This protects other parts of the headlight assembly.
Their compatibility with adaptive headlight technology is great for features such as beam shaping, automatic switching between high and low beams, and improved illumination when cornering.
When properly implemented, the extra brightness, improved beam control, and longer lifespan make LEDs an inexpensive solution that makes driving safer.
Different Types of Chips Used in Automotive Lighting
Automotive LED bulbs differ significantly from each other. You may be aware of differences in the shape, size, cooling system, and position of LED chips.
However, different LED chip types are also used in the automotive lighting industry and beyond and this makes a big difference.
COB (Chip On Board)
Chip-on-board LEDs are LED chips that are bonded directly to the substrate or printed circuit board instead of being connected by wires or soldered on like surface-mounted diodes. This approach allows more LED chips to be packed into an array.
A COB LED emits more light from the same area than a similar-sized surface-mounted diode. The light from COB LEDs is also more uniform since it comes from many more individual points of light within the same area.
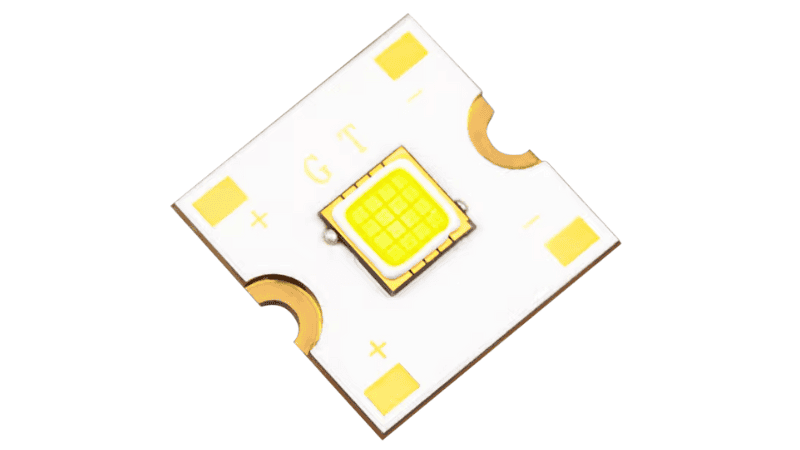
These chips have a layer of silicone that contains a yellow phosphor material. It enables them to transform the blue light into white light. All the chips in a COB array are energized using only two contacts. The substrate can be made from aluminum, sapphire, or glass.
Pros of COB LEDs
- They are more compact than SMDs and can be tightly packed, resulting in a greater light output per unit area.
- They have fewer points of failure because of the lack of wiring or solder, and the fact that they only need two contacts to energize the whole array.
- They produce less heat due to the lack of wires and soldering, and heat transfer from the chip is also more efficient.
- They have better viewing angles due to the lack of traditional LED packaging.

Cons of COB LEDs
- They are more expensive than traditional LEDs
- They are not small enough for some applications
- The color isn’t always consistent, especially in low-quality COB LEDs
- They are difficult to manufacture.
CSP (CHIP SCALE PACKAGE)
Chip Scale Package LEDs are LED chips with an overall package size that’s no larger than 1.2 times the size of the die.
CSP LEDs’ components don’t require wire soldered connections. This reduces failure points but also improves the LED’s thermal performance.
CSP LEDs’ configuration is different from surface-mounted LED chips which had to be connected to the printed circuit board using a wire. These wires can be damaged by heat or a power surge.

Mounting CSP chips on the substrate directly causes less thermal resistance. CSP chips are small but can produce more light and less heat than SMD LED chips.
Pros of CSP LEDs
- They have fewer points of failure than surface-mounted LEDs
- They transfer heat to the heat sink more efficiently than SMD and COB chips.
- They are smaller than COB chips and can be used for applications that need more compact LED designs.
- They produce a more uniform light beam compared to COB LEDs
- They have greater design flexibility than COB LEDs since they have even fewer components
Cons of CSP LEDs
- They are harder to manufacture than COB LEDs
- They are more expensive than COB LEDs
Philips ZES Chip
The Philips ZES chip is now called the Luxeon Z ES. It is a high-powered chip measuring 1.6mm by 2mm. The size of the chip gives it excellent design flexibility in different lighting applications.

This chip has been in the market since 2013 and continues to impress. It offers a better color consistency and light beam pattern than more recently developed chips. This is due to the excellent manufacturing standards of the company that makes them.
Pros of CSP LEDs
- Excellent manufacturing quality
- Good light quality
- Good beam control
Cons
- These cost more despite the age of technology
- They are not as bright as some newly developed chip designs.
CREE-Type LED Chips (Beaded)
CREE LED Chips refer to LED chips with a distinct clear sphere that covers the chips. This style of chips is usually associated with the manufacturer CREE. These LED chips are very energy efficient and produce little glare. They also have good focus.
Original CREE LED chips are premium products with excellent durability and consistent performance. They have specific chips designed for automotive LED lighting.
Pros of CREE-Type LED Chips
- Light output is crisp and focused with little glare resulting in good visibility for high beams
Cons of CREE-Type LED Chips
- This style of LED chip can be expensive
- They can’t use too much power and this limits their brightness
- Can be difficult to match with headlights for low beams
Flip Chip

As the name suggests, flip-chip LEDs are mounted upside down compared to surface-mounted chips. The result of this unique mounting method is that the LEDs can be attached without wires resulting in even more efficient heat dissipation.
These chips are also smaller and are the preferred option when compactness matters. The concept of mounting diodes upside down has been around since the 60s when it was used for transistors. The technology can be paired with CSP and COB.
Pros of Flip Chip
- Offers better heat dissipation than upright-mounted LED chips
- Doesn’t need wires for connections reducing points of failure
- The size of the chips is smaller in both height and area
Cons of Flip Chip
- The unique mounting style of these chips increases manufacturing complexity and cost.
The Size of LED Chips
LED chips come in sizes usually indicated using numbers such as 5050, 3528, or 2835. In these examples, the first two numbers indicate the length of one side of the LED and the second two numbers indicate the length of the other side.
For example, a 5050 LED chip is 5.0mm by 5.0mm and a 2835 LED chip is 2.8mm by 3.5mm.

When it comes to LED chip size, bigger doesn’t always mean brighter. Each chip can hold one or multiple diodes. This will affect the total lumen output.
Additionally, diodes are oriented differently on the chips and are made using different technologies. Therefore, a smaller LED chip might still be brighter than a larger chip while using less power.
Small chips can also be packed tighter. This will increase the light output per unit area.
The sizes of LED chips indicated by manufacturers are not a good measure of how much light the chips can produce especially since the measurements are for the chip, not the diode. Additionally, in a headlight bulb, a smaller diode may be more compatible.
Other LED Light Bulb Components

LED chips might be the key component of LED light bulbs but their performance will greatly depend on the quality of assembly/manufacturing and the quality of other bulb components. These other components are explained below.
Base assembly
This is the part of the bulb that connects it to the wiring of the car. It should have a connector that’s compatible with the vehicle’s wiring.
Heatsink
The heatsink is a critical component of LED light bulbs because heat lowers the durability and brightness of LEDs. Heatsinks can either have a fan or be fanless. Fans dissipate more heat allowing bulbs to draw more power and get brighter.
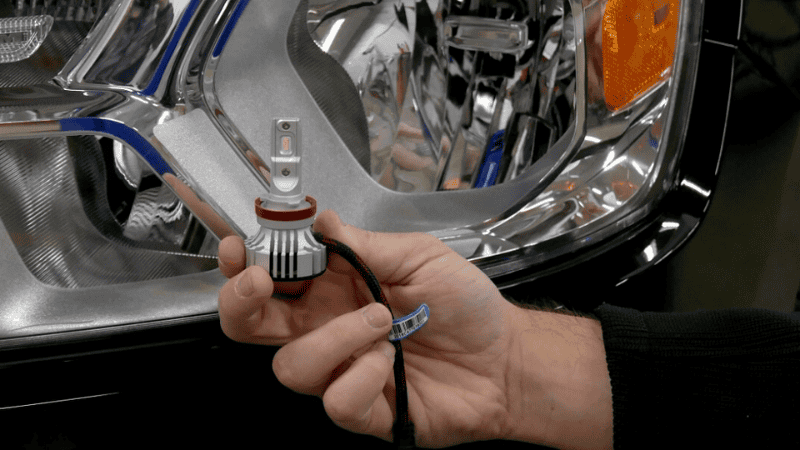

Heatsinks must be properly sized to offer adequate cooling at the bulb’s optimal operating brightness. Incorrectly sized heatsinks will not dissipate enough heat causing the chips to overheat and output less light.
LED Driver
The LED driver regulates the power that goes into the LED. LEDs require direct current while the car’s alternator produces alternating current. The driver handles both the conversion of current as well as limiting the current to protect the LED.
LED drivers can either be part of the bulb or attached to the bulb via a cable. When the driver is part of the bulb assembly, it can be affected by the heat from the LED chip.
CANbus Module
The CANbus module prevents your vehicle’s CANbus system from showing incorrect error messages when you install an LED bulb in a vehicle that comes with halogen bulbs.
LED bulbs with CANbus modules are only necessary for vehicles with CANbus systems. Many bulbs have built-in CANbus warning cancellers, but you may need to buy a separate one depending on your vehicle type.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
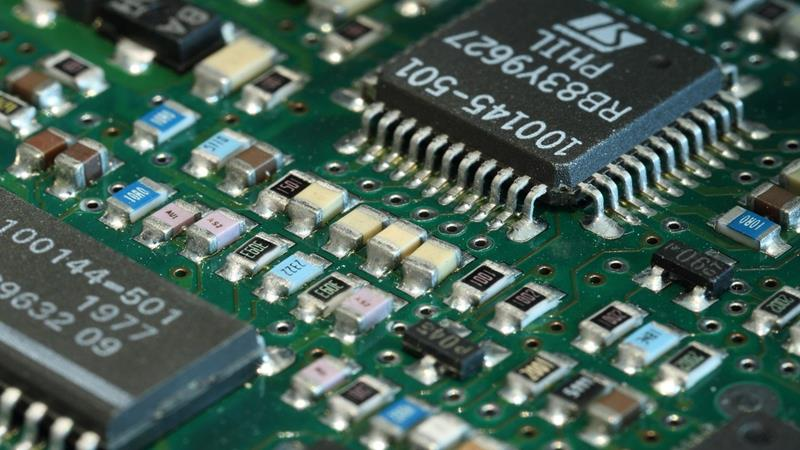

This is the substrate onto which the LED chip is mounted. It can be made from materials such as aluminum, sapphire, silicon carbide, and silicon. The substrate material varies depending on the application.
Optics
This is a cover that’s placed on top of the bulb similar to the glass bulb in traditional incandescent bulbs. This can be a diffuser or lens that helps to distribute the light from the LED. The bulbs used in LED headlights don’t usually have these covers. This job is performed by the headlight housing instead.
Conclusion
LED light bulbs have a simple design, but this simplicity hides the complexity of the technology behind them. The most complex part of the bulb is the LED chip. Different types of chips can be used for this application with different results.
Some chips come with the benefit of being less expensive, while others are more expensive but offer better performance. Ultimately, although the chip’s characteristics are important, what the light bulb manufacturer does with the chip will be just as important.
Reliable LED Chips – Contact Us Today
At Carlightvision, we can help you make sense of the technology inside these bulbs so you can make the right decisions when ordering your headlights. Contact us today so we can demystify LED chips for you.




